All record operation are made by the php data access class "data_accessclass".
The configuration for the table is saved in the JSON datadefinition.
As database My SQL is used.
The advantages are:<\p>
- control of the data access
- access class for all tables with individual configuration and includes
- access control to different users and roles
- supports objects, thanks to child configuration
- validation thanks to the table declaration (datadefinition)
My SQL
For support of the data access class the table structure has to follow this rules:
- primary key, INT, autoincrement
- creatorID, INT, if right check is needed
- datetimecreated, DATETIME (optional)
- clientID, INT (optional, needed for domain_rightmode=1)
- rightgroupID, INT (optional, needed for domain_rightmode=2)
- companyID, INT (optional, needed for domain_rightmode=3)
It's recommeded to add a second unique key:
- display column, VARCHAR unique, as identifier in links
| Table | Comment |
|---|---|
| k8login | The user table with login parameters and roles for the data access |
| k8loginfriends | sub table of k8login to add friends or follower |
| k8references | here are all uploads stored |
| k8languages | this is the place for translations in the database. The frontend translations are made in JavaScript. |
The users are saved in k8login.
Data access can be granted for friends or followers in k8loginfriends.
Images for all tables are joined in k8references.
Basic pages and datadefinitions
| Page | Datadefinition | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| register | k8loginregister | backend datadefinition: k8login |
| mydata | k8login | main definition for the form |
| k8loginfriends | for the friends table (lineedit) | |
| k8loginsearch | for the search of users, only userID and username | |
| user_list | k8login | user list for the admin |
| not yet available | k8references | images and attachments are stored here |
| not yet available | k8languages | translation for the backend |
If you like to change this datadefinitions, copy it please in your project folder. The datadefintions in the project folder are read first and have priority.
JSON datadefinition
This is the important configuration for the backend:
Main parameters
The main parameters are "table" and "primary key column". For the data access the class "data_accessclass" is used. This class is stored in the file "class_data_accessclass.php". This can be replaced by your own class. The rightcheck can be activiated. The details for it are placed in masterdata.
columns
Only the columns with the property "FIELD" can be inserted or updated. The data type is important for the header filter and the validation.
SQL Statement (sql_statement, sql_derived)
With a view more tables can be joined and columns can be added for the "read" method. The columns added by the view can not be inserted or updated. In the "sql_derived" the statement is nested. It's a bit slower, but easier to handle because you have all columns in the WHERE Statement.
rights
Each user can have several roles. Each role can have a method for the granted rights.
upload
If the upload is enabled, an array "imagearray" is added the recordset.
include
Thanks to the include individual functionality can be added.
backend / foreignkeys
Before the record will be deleted, foreign key can be checked. If the record is referenced by other tables, the deletion will be canceled and a message (text) is returned.
childs
All records of the child table are added with the "fieldname" to the main record. The childs can be nested and all parameters can used like for the main table.
parentcolumn
"parentcolumn" activates the reading of a tree structure. The "parentcolumn" contains the ID of the parent record. All records with the parentID are added in the array "treearrayname".
treearrayname
All records with the "parentID" are added to the array of this example: "_children".
Columns
| Property | description |
|---|---|
| fieldname | column name |
| mytype | Type without brackets |
| size | value between Type brackets |
| mydefault | set only to overwrite the column default |
| noupdate | true / false (not valid for admin) |
| noinsert | true / false (not valid for admin) |
| required | true / false |
| Field | column name in the table, empty -> not inserted or updated |
| Key | Example: PRI |
| Type | type of the column: varchar(50) |
The columns array is the basic structure to build the SQL-Statements. For a 'SELECT' the column definition is used to build up the WHERE part. In this case only 'fieldname' and 'type' is needed. Without definition the column is handled like 'varchar'.
filter types:
- VARCHAR: all char types
- NUMBER: TINYINT,SMALLINT,MEDIUMINT,BIGINT,INT,FLOAT,DOUBLE,DECIMAL
- BOOLEAN
- DATE
- DATETIME
- TIME
In an 'Update' or 'Insert' statement only the columns with the 'Field' parameter are written.
The 'creatorID' is always filled with the logged in userID ($_SESSION['userID']).
mydefault with asterisk, example: 10000*
The field is automatically incremented with the maxnumber()+1.
SQL statement
sql_derived example:
Please write the sql_statement or sql_derived in the datadefinition in one line (JSON compliant)!
The "sql_derived" property is important by using the view with tabulator, otherwise the property "sql_statement" should be used because it's a little bit faster.
The placeholder are:
- §select: additional fields are inserted:
- rightuser_update
- rightuser_delete
- '' as k8select: same §select
- §dateformat: the SQL date string is inserted
- WHERE 1=1: Where condition, here the "WHERE ".$clause is inserted
- §userID: $_SESSION['userID']
- §clientID: $_SESSION['clientID']
- §companyID: $_SESSION['companyID']
- §domain_language: $GLOBALS['domain_language']
Alternatively the include "getEntries_sql" can be used to write the statement direct in php.
Avoid to extend the sql statement (select or from section) in the properties: sql_statement or sql_derived. Please, use sql_additionals instead.
the column array is extended by additional columns:
columns
If the sql statement is extended with new columns, the data type needs to be declared, to get a correct filtering. Without declaration the columns are treated like 'VARCHAR'. It's also necessary for a list of available columns, like in the chartjs assistant.
In the example above, the column note is added. It is treated as boolean field. The fieldname is set; the "Field" column is only set for table columns.
sql_additionals:
select
The select part contatains the colums:
- <column name>: expression
aggregat
The columns with the aggregation are added by the chartjs assistant to the sql statement (sql derived).
from
The from part contatains the joined tables:
- alias or table name
- table: table name (default: alias)
- join: LEFT OUTER JOIN (default)
- expression: the ON part
By extending the SQL statement in a JSON data structure, its handling and readability are simplified.
Data access rights
RBAC (Role Based Access Control) assigns the user to 1 or more roles. Roles restrict or authorize the access to tables and records. This rights can only be granted by using the login with php sessions. The RBAC is implemented in the PHP data access class. The access check is activated for an object in the datadefinition by setting "rightcheck=1". In the data table the column "creatorID" is added. Comparing the creatorID with the logged in user gives the result: own record or foreign record.
By opening the website the user is assigned to the role "0:public". His userID is also 0. By login the role is replaced by the default roles of the login table: k8login.roles="3,5". The userID is set. For each object or table, for each CRUD operation (create, read, update, delete) and role an access check is implemented.
This is the data access definition in the datadefinition (masterdata.rights):
- CRUD Operation
- Role-ID
- Method for access check
- Role-ID
Thanks to the roles and data access methods, you can easyly grant the rights of your CRUD operations.
RBAC with K8 Web Kit
Roles
$GLOBALS[domain_roles]:
- roleID:
- name
Users and role membership
table k8login:
- userID
- roles (roleID-1, roleID-2)
comma separated roleIDs
Datadefinition / table
- CRUD Operation
- Role-ID
- Method for access check
- Role-ID
Methods
- 0: not granted
- 1: table.clientID=SESSION[clientID]
- 2: granted
- ...
- 10: table.creatorID=SESSION[userID]
Roles
The roles are defined in:
- config/_init.php
Users and role membership
The initial roles are the default value in the columns array of the datadefinition "k8login". It can be changed in the user list by super user or admin.
Datadefinition / table
In the datadefinition the rights are written in:
- masterdata
- rights
Methods
The methods are checked before or by executing the sql statement.
| Operation | SQL command | data access function |
|---|---|---|
| Create | INSERT | add() |
| Read | SELECT | getEntries() |
| Update | UPDATE | update() |
| Delete | DELETE | delete() |
By each CRUD operation the data access is checked in the correspondent data access function.
| ID | Role | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | public | user not logged in |
| 1 | admin | all rights in a client |
| 2 | superuser | all rights in the database |
| 3 | member | logged in user |
| 4 | employee | logged in user |
| 5 | friend | assigned in table: k8loginfriends |
| 6 | company, own data | domain_rightmode=3 |
| 7 | company, admin | domain_rightmode=3 |
| 19 | company login | domain_rightmode=3 |
| 21 | company read | domain_rightmode=3 |
| 25 | company create standard | domain_rightmode=3 |
| 30 | rightgroups | assigned in tables: k8rightgroups, k8rightmembers |
| x | others | create by yourself |
config/_init.php, domain_roles:
The available roles are defined in the "../config/_init.php".
Roles by login:
Each user can get assigned to 1 or several roles. The default roles can be set in masterdata/k8login/k8login.json, property: columns / roles / mydefault in a comma separated string like "3,5".
Admin / user list:
Superuser or admin can change the user roles in the user_list.
| Number | Check method |
|---|---|
| 0 | no rights |
| 1 | access permission in this client: table.clientID=$_SESSION[clientID] |
| 2 | permission granted |
| 3 | user logged in: $_SESSION[userID]<>0 |
| 4 | table.companyID=$_SESSION[companyID] |
| 5 | table.creatorID=$_SESSION[userID] table.companyID=$_SESSION[companyID] |
| 10 | table.creatorID=$_SESSION[userID] |
| 11 | check friend k8loginfriends.friendID=$_SESSION[userID] |
| 13 | checks membership in right groups |
| 14 | checks the rights of the active right group (rightgroupID) of the user: create: k8rightmembers.rightgroupID=$_SESSION[rightgroupID] and k8rightmembers.userID=$_SESSION[userID] and status>1 read: $table.rightgroupID=$_SESSION[rightgroupID] and k8rightmember.userID=$_SESSION[userID] and status>0 update: $table.rightgroupID=$_SESSION[rightgroupID] and k8rightmember.userID=$userID and ((k8rightmembers.status=2 and $table.creatorId=$userID) or k8rightmembers.status=3)) delete: same update |
| 1000 | check parent table access rights |
| ... | programm your own check |
By each CRUD operation the access rights are checked. If the operation by Create, Update or Delete is not granted, an error is returned. Reading a table can return an empty recordset, because of the missing rights.
By Read the results of the access check for Update and Delete are returned in advance like this:
- in the datadefinitition:
- masterdata.rightuser_create: true
- by reading the recordset:
- rightuser_update: true
- rightuser_delete: true
To check the user right by foreign tables the table can be joined or checked by "EXISTS()":
Access methods can depend:
- on a column of your own table
- or depend on a column of a joined table
This are the default rights (config/_init.php):
| Roles | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Operation | 0: public | 1: admin | 2: superuser | 3: member |
| Create | 0 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| Read | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| Update | 0 | 1 | 2 | 10 |
| Delete | 0 | 1 | 2 | 10 |
table cell = access method:
- =0: denied
- >0: granted by the method
The default rights are declared in the _init.php. They can be overwritten in the datadefinition.
datadefinition:
- masterdata
- defaultrights=true (default)
- rights
- create
- "0":2
- ...
- ...
- create
masterdata/_init.json
This are the default rights of the initialization.
Rights from the datadefinition overwrite the default rights. To allow the roles, public and member, to read all records in the object, add in the datadefinition:
The following rights are changed:
- create:
- 0: public
- 2: granted, can register and add a record
- 0: public
- read:
- role "0" public is not allowed to read the data
- update / delete:
- same, like default
Rights from the datadefinition overwrite the default rights. To allow the roles, public and member, to read all records in the object, add in the datadefinition:
Rights from the datadefinition overwrite the default rights. To allow the roles, public and member, to read all records in the object, add in the datadefinition:
| Roles | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Operation | 0: public | 1: admin | 2: superuser | 3: member | 4: employee |
| Create | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| Read | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 2 |
| Update | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 10 |
| Delete | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 10 |
table cell = access method:
- =0: denied
- >0: granted by the method
The default rights are declared in the _init.php. They can be overwritten in the datadefinition.
Attention:
The rigths for public tables, for example: "k8pages", need to be changed!
Rights from the datadefinition overwrite the default rights. To allow the roles, public and member, to read all records in the object, add in the datadefinition:
This are the default rights for a scret company in json!
The access right of the table depend on another master table. In this case the master table needs to be checked for the access rights. This is declared in the datadefinition:
Link to master
The masterdatadefID declares the master datadefinition. The first right check is made by this datadefinition. The masterkey defines the colun of this table, which correspond to the master key column of the master datadefinition.
Access right: read
- first the acces rights of the master is checked
- The right of the master is heritated to the child by the method: 1000
Access rights: create, update, delete
- first the right "Update" of the master is checked
- The right of the master is heritated to the child by the method: 1000
In this example the the access for role 2 is granted to all CRUD methods. The role 3 herites the access from the master.
Using clients
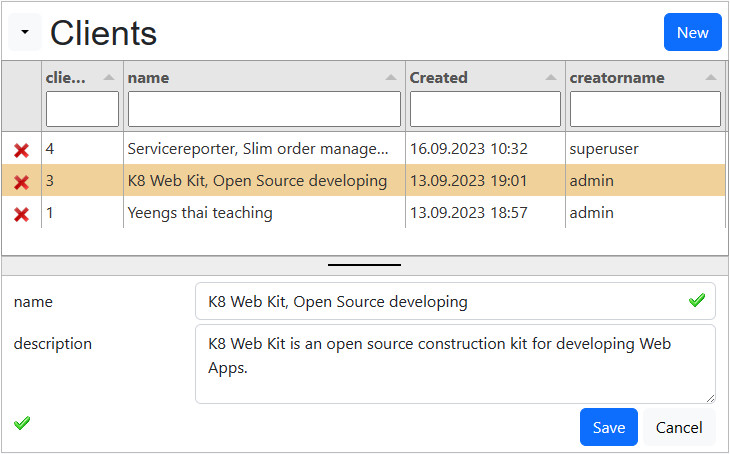
Allow multiple clients to use your Web App. Each table has a clientID to differentiate the data from each other. Each Client has an own admin to govern his data and user. The user registers for 1 client. For each client he needs a different email.
Preparation
config/_init.php:
The domain_rightmode==1 enables:
- register: selection of the client
- menu Admin: display "Clients"
Social groups (right groups)
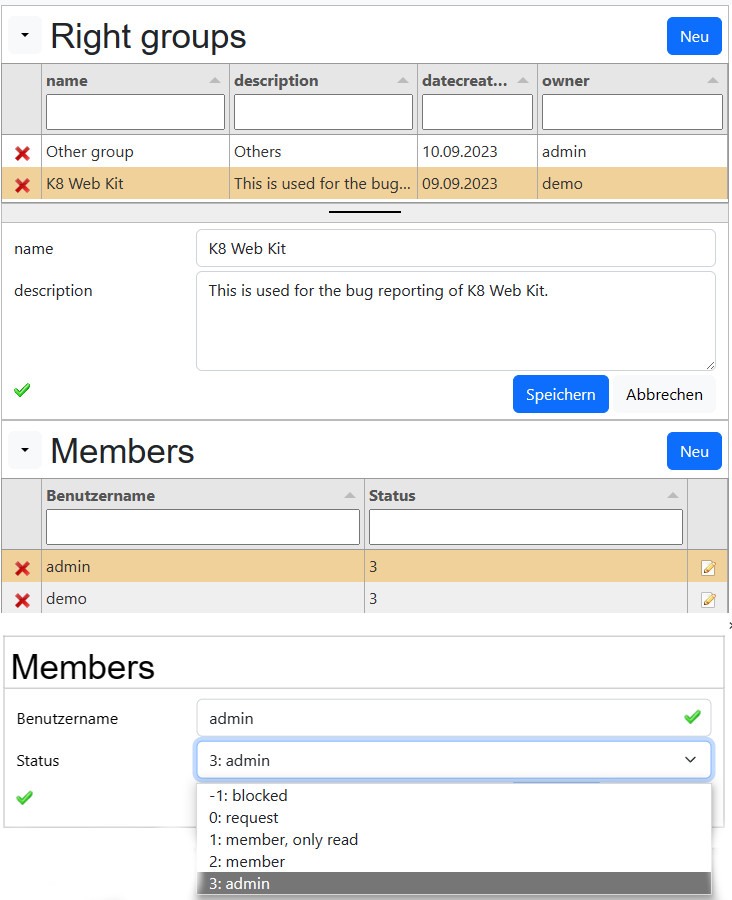
Social groups are part of many social platforms like facebook and others. Properties of a social group are:
- Title
- Description
- Owner
- Picture
- Members
- Admins
- Observers
- Members
This are the involved datadefinitions:
- k8rightgroups: the group header (folder: masterdata)
- k8rightmembers: the group members (folder: masterdata)
- your table: for example the postings
The rights of the member are defined in the column "status" in "k8rightmembers".
The data access methods are:
- 13: all records with group membership
- 14: filtered to rightgroupID in SESSION
Create a group
- Users with the role 30 have the right to create a right group
- the creator is added as admin
Frontend
- User
- Listing of his groups: membership
- Right group catalog
- Right group form
- Member list (request)
- Admin
- Masterdata form with all groups
13, right group is added by the form
Attention:
- rightgroupID needs to be a field in the form!
This is the "right" definition of the masterdata section:
14, filtered to rightgroup in SESSION
Attention:
- right group has to be choosen in My data (SESSION variable)!
This is the "right" definition of the masterdata section:
By writing a new record the rightgroup is filled automatically with the SESSION rightgroupID.
Your datadefinition
Your table need to contain the column:
- rightgroupID(INT), attention no update
You need to define special rights:
- look above, rights for method 13 or 14
The Menu
The following variables are available in JavaScript:
- dat_user.roles: create a special role for your rightgroups
- rightgroupID: the SESSION[rightgroupID]
- GLOBALS_config['rightidentifiers']: array with all identifiers of the rightgroups with membership.
Preparation (14)
config/_init.php:
The domain_rightmode=2 enables:
- my data: selection of the right group
- data access class:
- validation: check the right group
- add: adds the rightgroupID from SESSION variable
Example for right groups (13): Bug Reports

Elements of Bug Reports:
- Projects
- table: k8projects
- datadefID: projects
- Bug Reports
- table: k8bugs
- datadefID: bugreports
- Bug Fixes
- table: k8bugfixes
- datadefID: bugfixes
Data access:
- Roles:
- 101: Bug fixes
- rightgroups:
- identifier: Bug Reports
Right groups in master data form (13)
The project in the head is assigned to a rightgroup. Without project no new records are allowed. After selecting the rightgroup the rights are checked. The records are displayed. If the create right is granted, a new record can be added.
Example for projects (13)
extract of project datadefinition:
The following rescources are added:
main
- JavaSript file: projects_head_end.js
- datadefinitions: k8rightgroups
masterdata
- the rights are defined
- the SQL statement is expanded with rightgroupname
tabulator
- the rightgroupname is added to the columns
k8form
- the form element rightgroupname is added as datalist
JavaScript:
The following configurations are made:
- GLOBALS_rightmode==2 (14)
- rightgroupname is not displayed
- GLOBALS_rightmode!=2 (13)
- Button "New" is activated
Company with employees

Allow companies to create an account and to add employees:
Own data access methods
| Operation | Function | Return values |
|---|---|---|
| Create | bRecordAccess() | true / false |
| Read | bRecordReadPermission() |
$out[]:
|
| bRecordUDPermission() |
$out[]:
| |
| Update | bRecordAccess() | true / false |
| Delete | bRecordAccess() | true / false |
bRecordReadPermission()
This function creates a clause which which determines which records are read.
bRecordUDPermission()
This function is called 2 times and creates the columns for the data access "update" and "delete":
- rightuser_update: 0/1
- rightuser_delete: 0/1
In config/_init.php the variable $GLOBALS['domain_includes'] allows to include own PHP files to write your own methods:
- [RBAC_Read]:bRecordReadPermission()
- [RBAC_RUD]: bRecordUDPermission()
- [RBAC_CUD]: bRecordAccess()
childs
childs definition of the invoice eaxample:
By declaring a childs array or nested childs arrays, an object with several arrays can be read and written to the database. The definition of a child is same to the master. If no columns array is added for the child, it is generated on the fly out of the table structure. Please regard this properties:
- fieldname: "items" in the invoice example for all records of the k8documentitems table
- masterkey: the column corresponding to the key column of the parent table
- richtcheck: 0, no rightcheck for the childs
Avoid SQL injection
What is SQL injection
SQL injection (SQLi) is a web security vulnerability that allows an attacker to interfere with the queries that an application makes to its database.
- expression in clause
- UNION expression
- more to SQL inection:
Avoid clause
In developement a clause is fast written down. To reduce the risk of SQL injection, the following measurements are taken in PHP:
- clause in brakets
- remove comments: /* */ -- #
- use db->real_escape_string($value)
config/_init.php
developement:
- 0: clause is ignored
- 1: clause is executed
Attention: If you turn off your developement, clauses from the query string are no more accepted!
Sorting
sort array
With the sort array the sort fields are transfered to the backend:
In PHP the sql statement, part order by is build like:
- ORDER by name1 desc, city
Filtering
filters array
With the filters array the filter fields are transfered to the backend:
In PHP the clause is created like this:
- $clause="rightgroupID=1";
There are 2 variables for filters:
- filters: for the WHERE clause of the main SQL statement. If it's a derived statement the column name is without table preset otherwise with table preset.
- filtersin: by an SQL derived statment, it is placed to the inner SQL statement
filters array with or
With the filters array the filter fields are transfered to the backend:
A nested filters array is added with "or":
- rightgroupID=1
- or rightgroupID=2
Complex filtering with PHP include
datadefinition:
The SQL statment is build in PHP by an include file. The file is declared in the datadefinition:
Example: masterdata/k8rightmembers/k8rightmembers_getEntries.php
buildclause
By the query parameter "buildclause" an expression "EXITS(...)" is added to the SQL statement.
JavaScript:
In JavaScript the parameter buildclause is added to the property: data_readfilter.
ProcessData.php
Parameters
All ajax requests are send to "ProcessData.php".
- process_action
- datadefID
- additional parameter:
- filters[]
- sort[]
- clause (deprecated)
- keyvalue
- arr
- prefix
GetObject
process_action=GetObject&datadefID=<yourdatadefID>
It returns the datadefininition in the data property:
ReadFilter
process_action=ReadFilter&datadefID=<yourdatadefID>
additional parameters:
- filters[]
- field
- type
- value
- filtersin[]
- sort[]
- clause (deprecated)
- clausein (deprecated)
- mytable_offset
- mytable_limit: only set, if mytable_offset is also set
It return the the records:
If mytable_limit is not set the maximum returned records are limited by $gdatareadlimit(50).
Load
process_action=Load&datadefID=<yourdatadefID>
additional parameters:
- keyvalue=<keyvalue>
It returns the result "bok", the error or the record "dat".
Save
process_action=Save&datadefID=<yourdatadefID>
additional parameters:
- object with form fields
If the primary key=0 a new record is inserted, otherwise the record is updated. It returns an error or the saved record:
Delete
process_action=Delete&datadefID=<yourdatadefID>
additional parameters:
- keyvalue=<primarykey>
It returns "bok" with the the keyvalue or 0 by an error with the error message: